Hydrogen is gaining significant attention as a key energy carrier in the transition to a sustainable energy future. Hydrogen presents a zero-emission alternative to fossil fuels, making it an attractive option for decarbonizing various sectors, including transportation, industry, and power generation. However, the challenges associated with hydrogen measuring require advanced and precise instruments to ensure safe and efficient applications, where the pressure measurement is particularly important.

What Regulatory Standards Point to the Importance of Hydrogen Pressure Measurement?
The following are some key regulatory standards and guidelines related to hydrogen pressure measurement, which ensure safety, compliance, and reliability in hydrogen applications:
ISO 14687
This international standard specifies the quality criteria for hydrogen used in fuel cells. It includes requirements for pressure levels during storage and dispensing to ensure safe operation.
IEC 62079
This International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard provides guidelines for the preparation of instructions for the safe use of electrical equipment, including that used in hydrogen applications. The highlight is the importance of pressure measurement and monitoring systems in ensuring safe operations in hydrogen environments.
CSA B51
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) B51 covers the design, construction, and inspection of pressure vessels for hydrogen and other gases. It emphasizes the importance of accurate pressure measurement for safety and compliance in hydrogen storage and transport systems.
(Reference:https://midwestinstrument.com/2021/08/25/what-is-csa-b51-14-piping-codes-standards/)
EU 2021/892
This regulation(EU Regulation on the Safety of Hydrogen Equipment) addresses safety requirements for hydrogen apparatus, including comprehensive safety measures for pressure measurement systems in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution to minimize accidents.
What are the Challenges for Hydrogen Pressure Measurement?
The challenges of hydrogen pressure measurement are mainly caused by its special physical and chemical properties.
Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement, also known as hydrogen-induced cracking. Hydrogen molecules(H₂) can dissociate into two hydrogen atoms(H+) under catalysis when the molecules are adsorbed onto a metal surface. Hydrogen atoms penetrate into the metal structure. They gather inside the metal and exert pressure outward, causing the material to lose ductility, which in turn causes the metal to crack. The damage is irreversible.
Hydrogen Explosion
Compared with other common fuels, hydrogen has a wide flammable range. In the air, hydrogen can burn at concentrations between 4% and 75%. Hydrogen reacts very quickly with air and oxygen, releasing a large amount of heat energy in a very short time, causing fire or explosion.
Where is Hydrogen Pressure Measurement Needed?
Hydrogen Production
In the process of hydrogen production by water electrolysis, pressure monitoring is mainly concentrated in the following parts:
• Electrolyzer: Monitor the gas pressure at both ends of the electrolyzer to avoid overpressure, causing equipment damage or safety accidents.
• Hydrogen Outlet: Before hydrogen is collected and transported, outlet pressure monitoring ensures the gas is stable and meets the use or storage requirements.
Hydrogen Storage & Delivery
• Storage Tanks: Internal pressure monitoring of storage containers (such as high-pressure gas cylinders, hydrogen storage tanks, etc.) avoids the damage or explosion of the container owning to overpressure.
• Connection Parts: Monitoring the pressure at the connection points, such as valves and pipeline joints, can detect leaks or abnormalities in time to ensure safety.
• Pipeline: Pressure sensors or pressure transducers are placed at key points along the hydrogen pipeline:
① Inlet Section: Near the hydrogen source or compressor station to measure the pressure entering the pipeline.
② Mid-Section: To monitor pressure along the pipeline length for leak detection, flow management, or pressure drops.
③ Outlet Section: Near the delivery point to the end-use facilities or storage tanks, the pressure transmitters ensure the system operates within safe and optimal pressure ranges.
Hydrogen Fueling Stations
• Hydrogen Filling Equipment Outlet: Hydrogen filling equipment needs to safely fill the vehicle with hydrogen at high pressure. The pressure transmitter at the hydrogen filling gun outlet ensures accurate control of hydrogen pressure during the filling process, improving filling efficiency and safety.
• Safety Monitoring System: Pressure transmitters in the safety monitoring system continuously monitor the pressure of hydrogen storage tanks and refueling equipment, preventing accidents caused by pressure anomalies. Once the instrument detects an abnormal pressure drop, it can quickly alarm and trigger safety measures.
What Does a Pressure Instrument Feature for Hydrogen Monitoring?
The core challenge of hydrogen pressure measurement is to balance safety and accuracy. Therefore, pressure instruments need to meet multiple requirements in material, explosion-proof certificated, and environmental control.
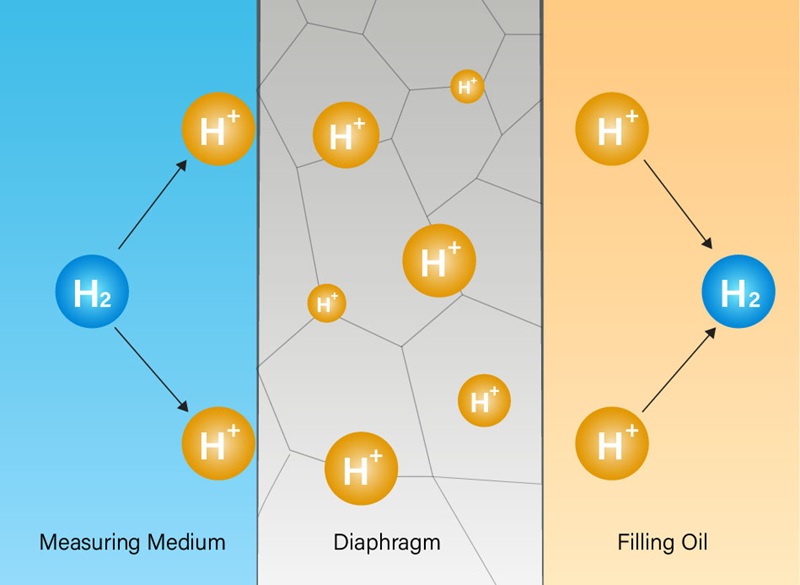
• Wetted Materials: 316L stainless steel or Hast C diaphragms are not sufficient to effectively prevent hydrogen penetration. Hydrogen penetration increases the risk of filling oil contamination and causes a decrease in hydrogen pressure measurement performance. The gold-plated diaphragm minimizes the diffusion of hydrogen atoms through the diaphragm.
• Explosion-proof Design: The instrument must comply with explosion-proof certification (such as ATEX, IECEx) to avoid electric sparks igniting hydrogen.
• Temperature Compensation: When hydrogen passes through a throttling device (such as a throttle or valve), its temperature rises. Therefore, pressure measuring instruments with good-performance temperature compensation can offset measurement errors or performance deviations caused by temperature changes.
Recommended Products
MPM480GH Pressure Transmitter for Hydrogen Measurement
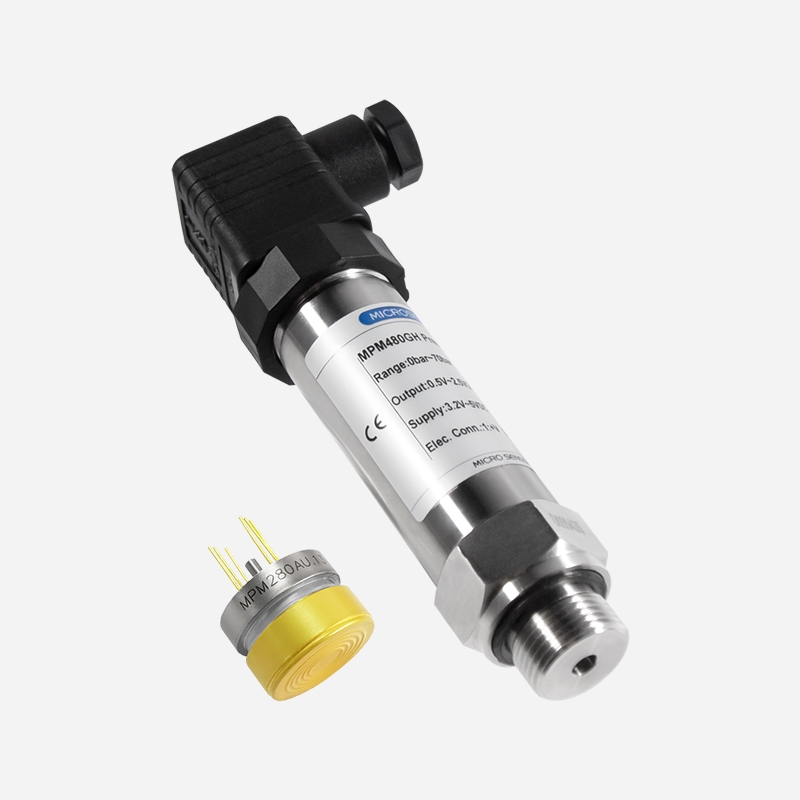 | • Inner sensor diaphragm is gold plated(MPM280Au), fully welded inner sensor assembly structure, effectively preventing hydrogen penetration • Support reversed-polarity, overcurrent and overvoltage protection, conforming to EMI protection requirements • Intrinsic safety type circuit, or use in hazardous areas • High accuracy, up to ≤±0.25%FS • Used For: Hydrogen Production System, PEM Fuel Cell, Hydrogen Fuel Cell Test Station, Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Test System |
The importance of precise pressure measurement in its applications cannot be overstated. It is integral to ensuring safety, efficiency, regulatory compliance, and the overall integrity of hydrogen systems. If you need more specific solutions or further information about hydrogen measurement, contact us for expert advice and customized recommendations!





























 Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD
Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD