New Product Change Notice (PCN) effective Jan 1, 2025. MICROSENSOR appreciate your understanding.
Magnetic Flowmeters
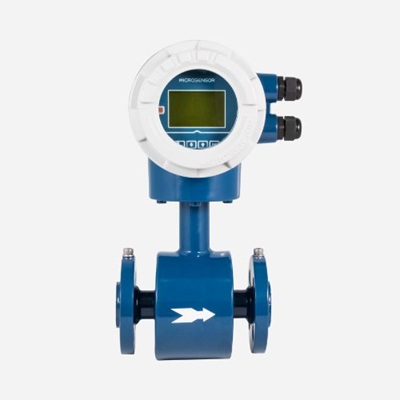
Electromagnetic Flowmeter
MFE600E
CE, ATEX approved
Flange, sanitary, threaded, clamping type available
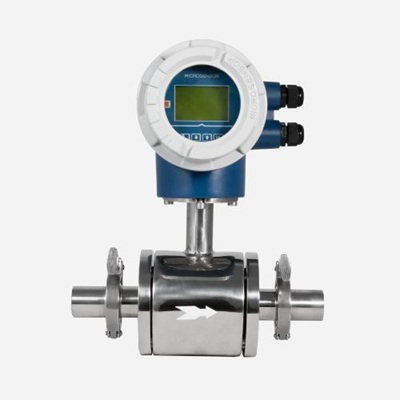
Electromagnetic Flow Meter
MFE600Z
Accuracy: ±0.5%, ±1.0%
Corrosion- and wear-resistant electrode and lining materials available
Corrosion- and wear-resistant materials available
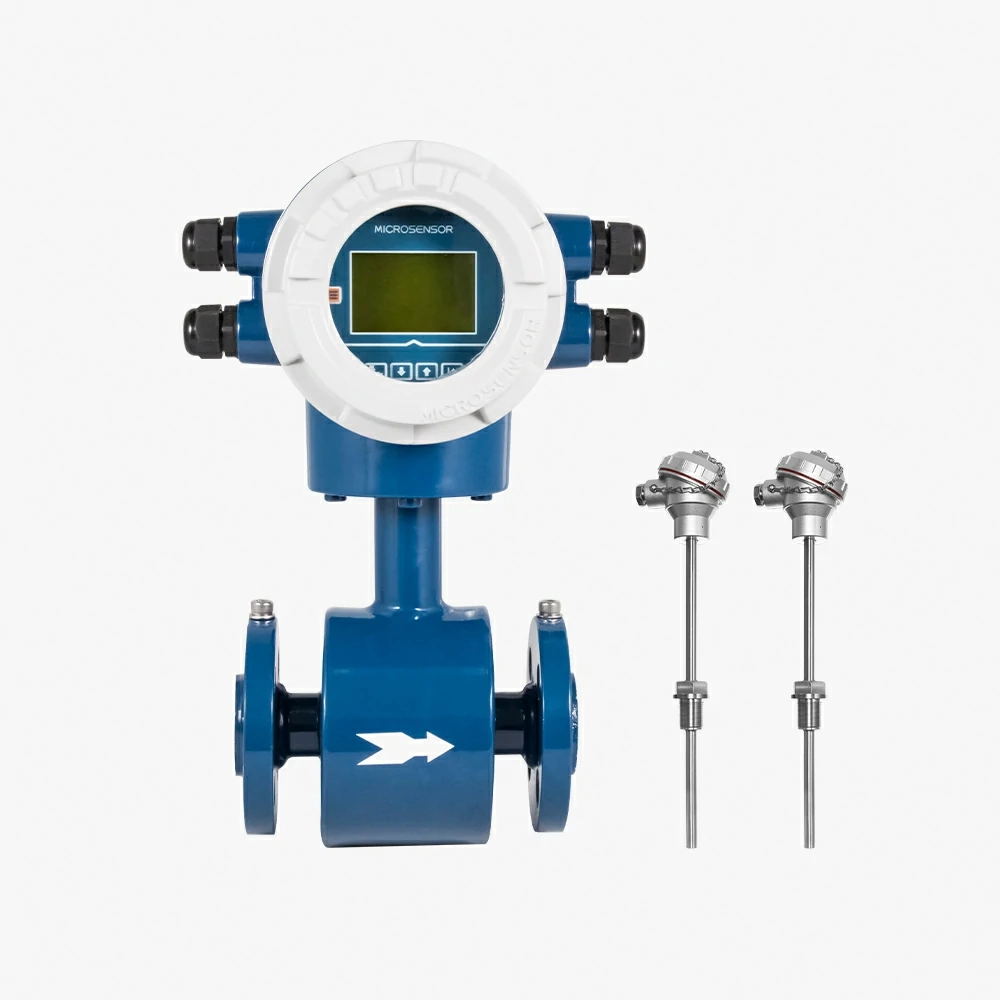
Electromagnetic Heat Flowmeter
MFE600H
Structure type: separated type, integrated type
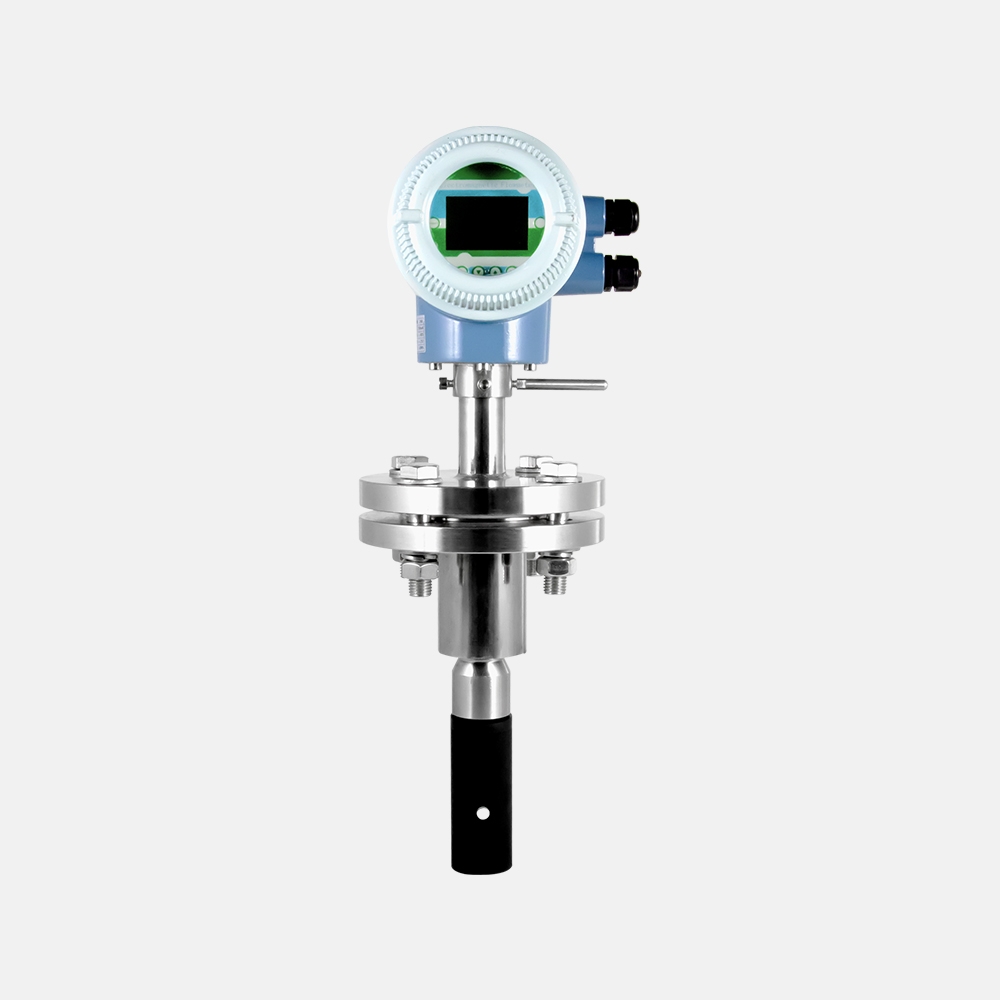
Insert Type Electromagnetic Flow Meter
MFE600C
Accuracy: ±2.5%
Convenient for maintenance and repair
Pressure port: ANSI 1/2 NPT, JIS G1/2
What is an Electromagnetic Flow Meter?
An electromagnetic flowmeter (EMF, often called a mag meter or magnetic flow meter) is a process instrumentation used to measure the volumetric flow rate of liquid inside a pipe. It is one of the most popular flow meters for conductive fluids due to its high accuracy, reliability, and no moving parts.
The magnetic inductive flow meter working principle is based on Faraday's Law of Induction. The operation can be broken down into a few simple steps:
1. Creating a magnetic field across a pipe.
2. Measuring a tiny voltage induced in a conductive liquid moving through that field.
3. Calculating flow velocity directly from that voltage, as they are perfectly proportional.
The Essential Checklist for Using a Magnetic Flow Meter
A magnetic flow meter is the top choice for conductive liquids in numerous industries. But how to check if it's the ideal solution for your applications? Start with the necessary key requirements:
✅ Fluid Conductivity
The fluid must have certain electrical conductivity, typically σ> 5 μS/cm.
Typical Suitable Media: Water, wastewater, acids, caustics, slurries, pulp, and many other process liquids.
Unsuitable Media: ①Non-conductive fluids like oils, gases, steam, or ultrapure water (which has very low conductivity). ②Liquid with a gas volume fraction exceeding 5-10%.
✅ The Medium Must Fill the Pipe
The meter calculates flow rate based on the average fluid velocity through the entire cross-sectional area of the pipe.
If the pipe is not full, the measurement will be inaccurate, leading to significant errors. They are not suitable for open-channel flow measurement unless paired with a specially designed flume or weir that incorporates a full pipe.
Advantages of Magnetic Flow Meters
✅No Obstruction to Flow: The magmeters have no moving parts or obstructions (like paddles or gears), resulting in a smooth and straight pipe without any components that obstruct fluid flow. Thus, no additional pressure loss occurs when fluid passes through.
✅Bidirectional Flow Measurement: Based on electromagnetic physics, a magflow meter doesn't need any special modifications to measure bi-directional flow(forward flow & reverse flow). The bidirectional flow measurement is useful in pipeline netting or backflush cycles, such as process control in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
✅High Accuracy: In comparison with other flow measurement technologies, the magnetic flowmeter typically has an accuracy of ±0.5%, or better up to ±0.2%. Also, the measurement accuracy is independent of the fluid's physical properties (such as density, viscosity, temperature, and pressure).
✅Easy Maintenance: No moving parts to wear out, jam, or break. No ports to become clogged. It drastically reduces maintenance needs and costs.
Application of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
MICROSENSOR offers a comprehensive electromagnetic flow portfolio, each engineered with specific connection types and features to meet the diverse requirements of various industries and application scenarios. Selecting the correct type is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, accuracy, and longevity in your specific electromagnetic flow measurement environment.
| Types | Applications | |
| Flange-Mounted | - Water Conservancy and Irrigation - Water Supply and Drainage - Pulp and Paper - Metallurgy/Chemical (explosion-proof) |
| Clamp-On | - Perfect for sanitary applications with quick-connect interfaces. - Food and Beverage |
| Thread-Mounted | - Suitable for small diameter applications. - Equipment Supporting / Equipment Matching |
| Battery-Powered | - For outdoor environment applications without current output. - Petroleum |
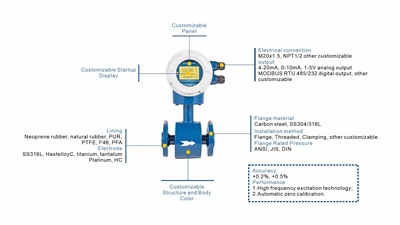 | Customized Magnetic Flowmeters | Customization Optional: - Liner Material - Electrode Material - Meter Body/Housing - Panel & Startup Display - Electrical Connection & Output - Installation Method ...... |
For any selection questions or to confirm suitability for your specific applications, we highly recommend professional consultation with our technical support team. Contact us now!
Electromagnetic Flowmeters from MICROSENSOR
MICROSENSOR is a global magnetic flow measurement manufacturer and supplier. Our types of electromagnetic flowmeters are designed for most industrial applications. Customized magnetic flowmeters meet specific requirements with a wide range of DN6 ~DN1600, multiple options for liner, electrodes, accuracy, etc. Powered by CE and ATEX certifications, our electromagnetic flowmeters represent a technology-driven choice from general-purpose water flow measurement to highly corrosive or abrasive slurries.
-
Why Does a Magnetic Flowmeter Deliver High Accuracy?
For industrial process control, accurate flow measurement is a necessity. Among the various flow technologies available, the magnetic flow meter (EMF) consistently stands out for its exceptional precision.
-
How to Correctly Install an Electromagnetic Flowmeter?
The installation of electromagnetic flowmeter is a complex process that requires careful consideration to ensure measurement accuracy and long-term stable operation.Precautions for installing electromagnetic flowmeter:1.The electromagn...
-
FAQ about Electromagnetic Flowmeter Selection
According to statistics from authoritative organizations in the world, two-thirds of the flow meter failure cases are caused by inappropriate product selection and on-site installation. Understanding the knowledge related to flow meter...
-
Common Troubleshooting for Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Common Fault 1: Why does the electromagnetic flow meter value change when the pipe is empty?Solution: ① Interference with the grounding. ② Whether there is water in the horizontal installation. ③ Whether there is backflow in the ver...
-
Application of Flowmeter in the Lithium Battery Industry
Industry ProspectsWith the increasing demand for the new energy vehicle market, various supply chain industries have surged. Among them, the lithium cell, as one of the most important components, accounts for 40%-50% of the overall cos...








































 Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD
Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD